Key fobs have become an indispensable component of modern automotive convenience, and Renault, a well-known automobile manufacturer, is no exception in offering this technology to its customers. However, with technological advancements come important legal considerations. This article will delve into the regulations and legal requirements related to the use and programming of Renault key fobs to ensure a clear understanding of the responsibilities and obligations that come with their use.
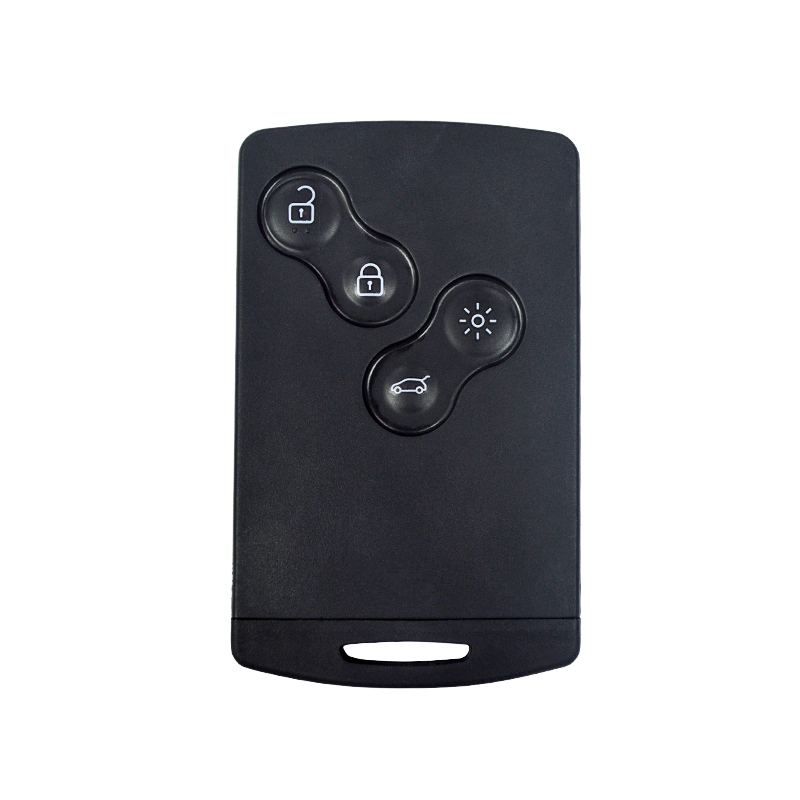

1. Emissions and Interference Regulations
Renault key fobs, like any wireless device, must comply with electromagnetic emissions and interference regulations. These regulations are in place to prevent wireless devices from interfering with other electronic systems, such as air traffic control or emergency services communication. To ensure compliance, Renault and other automakers must adhere to international standards set by organizations like the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States and equivalent authorities in other regions.
2. Data Privacy and Security
The use of key fobs, especially in modern vehicles with advanced connectivity features, often involves the collection and transmission of personal data. To safeguard customer privacy and data security, manufacturers like Renault must adhere to stringent data protection laws and regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. These regulations dictate how customer data is collected, stored, and used, and manufacturers must implement robust security measures to protect against data breaches.
3. Vehicle Theft and Security Regulations
Renault key fobs play a crucial role in vehicle security, as they are used for locking and unlocking the vehicle. To comply with anti-theft regulations, automakers like Renault must ensure that key fobs are secure and cannot be easily replicated or manipulated to gain unauthorized access to a vehicle. Additionally, there may be regional requirements related to vehicle security features, and Renault must adhere to these when manufacturing and programming key fobs.
4. Environmental Regulations
Environmental regulations apply not only to the vehicles themselves but also to the materials used in key fobs and their disposal. Key fobs may contain batteries and other electronic components that need to be disposed of responsibly to prevent environmental harm. Regulations may also govern the materials used in key fobs to ensure they are environmentally friendly.
5. Consumer Protection Regulations
Renault, like other manufacturers, is obligated to adhere to consumer protection regulations when it comes to the sale, warranty, and service of their key fobs. This includes providing clear information to customers about the capabilities, limitations, and potential costs associated with key fobs. Additionally, manufacturers must offer warranties and support services to address any defects or issues with the key fobs.
6. Patent and Intellectual Property Rights
Key fob technology often involves patents and intellectual property rights. Manufacturers like Renault must ensure that their key fob technology does not infringe on existing patents held by other companies. Additionally, they should protect their own patents related to key fob innovations to prevent unauthorized use by competitors.
Conclusion
The use and programming of Renault key fobs are subject to a complex web of regulations and legal requirements. These encompass various aspects, including emissions and interference regulations, data privacy and security, vehicle theft and security regulations, environmental concerns, consumer protection, and intellectual property rights. Adhering to these regulations is essential not only for legal compliance but also to ensure the safety, privacy, and satisfaction of Renault customers. As technology continues to advance, staying informed and compliant with these regulations is crucial for both manufacturers and users of key fob technology.

 Englishen
Englishen











 No.991 Xingxiu Road,Taiwanese Investment Zone, Quanzhou, Fujian Province,P.R.China
No.991 Xingxiu Road,Taiwanese Investment Zone, Quanzhou, Fujian Province,P.R.China +86 13960286508
+86 13960286508
 3D Reality Showroom
3D Reality Showroom
